Cricket scoring might seem overwhelming at first, but understanding the basics makes watching or playing the game far more enjoyable. This guide breaks down cricket's scoring system into clear, digestible pieces that anyone can understand.
What is Cricket? The Basics You Need to Know
Cricket is a team sport where two teams of eleven players compete to score the most runs. Here's what makes cricket unique: while the fielding team has all eleven players on the field, the batting team only has two players actively participating at any given time. These two batters work together to score runs while the fielding team tries to get them out.
The fundamental concept is simple: score runs by hitting the ball and running between two sets of wooden posts called wickets. The team with the most runs wins.

How Cricket Scoring Works: The Three Core Elements
Cricket scoring centers on three fundamental components that determine the flow and outcome of every match.
1. Runs: The Points System
Runs are the points in cricket. Batters score runs primarily by hitting the ball and running to the opposite end of the pitch. Each successful run between the wickets adds one point to the team's total. Think of it like scoring points in basketball, except players must physically run to earn each point.
2. Wickets: Getting Players Out
A wicket represents a batter being dismissed or "out." Each team has ten wickets to lose (since one batter must always remain not out). Once a team loses all ten wickets, their innings ends. Common ways to lose a wicket include:
- Getting caught by a fielder after hitting the ball
- Having the stumps knocked down by the bowler
- Being run out while attempting to score
3. Overs: The Time Units
An over consists of six consecutive balls bowled by one player. In limited-overs cricket (like One-Day Internationals), each team faces a set number of overs, typically 50 or 20. This creates time pressure and strategic decisions about when to play aggressively versus conservatively.

Advanced Scoring Concepts That Add Strategy
Beyond basic runs, cricket includes strategic scoring elements that create dynamic gameplay.
Extras: Free Runs from Mistakes
Extras are bonus runs awarded when the fielding team makes errors. Think of them as penalty points in other sports. Common extras include:
- Wides: Ball bowled too far from the batter to hit reasonably
- No-balls: Illegal deliveries, such as overstepping the bowling line
- Byes: Runs taken when the ball passes the batter without contact
- Leg-byes: Runs scored after the ball hits the batter's body
Boundaries: Quick Scoring Opportunities
Boundaries provide rapid scoring without running:
- Four runs: Ball reaches the boundary after bouncing
- Six runs: Ball clears the boundary without bouncing
Boundaries create excitement and can quickly change match momentum, similar to three-pointers in basketball.
Strike Rate: Measuring Scoring Speed
Strike rate shows how quickly a batter scores, calculated as (runs scored ÷ balls faced) × 100. A strike rate of 100 means scoring one run per ball faced. This metric helps teams balance aggressive scoring with preserving wickets.
Real-World Scoring Examples
Let's see how scoring works in practice:
Example 1: Running Between Wickets
The batter hits the ball into the field. Both batters run to opposite ends twice before the fielder returns the ball. Result: 2 runs added to the team total.
Example 2: Hitting a Six
The batter connects perfectly, sending the ball over the boundary rope without bouncing. Result: 6 runs automatically added, no running required.
Example 3: Combination Scoring
In a single over, a batter might score: one four (4 runs), two singles (2 runs), and face a wide (1 extra run). Total from that over: 7 runs.
Special Rules That Impact Scoring
Two important systems ensure fairness in modern cricket:
The Duckworth-Lewis Method (DLS)
When rain interrupts play, the Duckworth-Lewis method recalculates targets to maintain fairness. This mathematical formula considers:
- Overs lost due to weather
- Wickets remaining for the batting team
- Scoring patterns at that stage of the game
The DLS ensures neither team gains an unfair advantage from weather delays.
Decision Review System (DRS)
The DRS allows teams to challenge umpiring decisions using technology. Each team gets a limited number of reviews per innings. Technology used includes:
- Ball-tracking systems for LBW (leg before wicket) decisions
- Ultra-edge detection for caught-behind appeals
- Slow-motion replays for run-outs and stumpings
This system reduces human error in crucial decisions that affect scoring and match outcomes.
Understanding Cricket Scorecards: Your Complete Guide
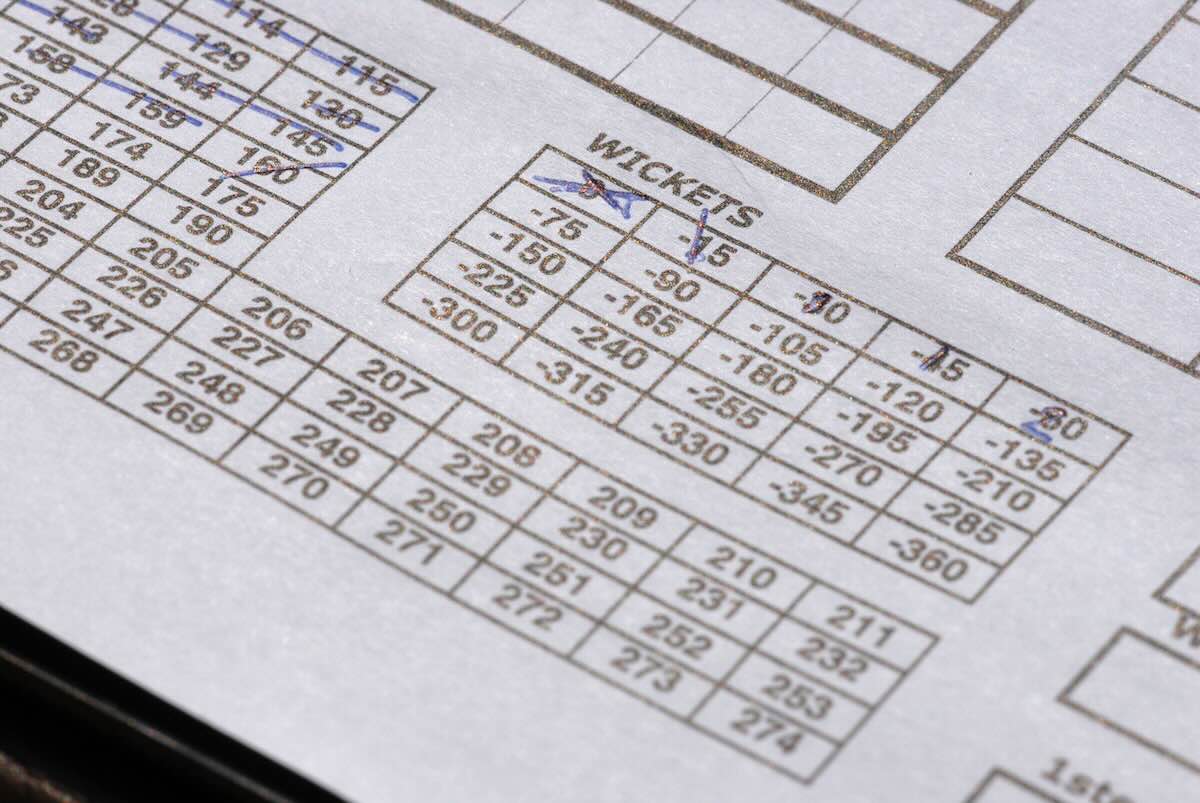
A cricket scorecard tells the complete story of a match. Here's how to decode each section:
Team Information
- Team names and toss result: Shows who's playing and who chose to bat or field first
- Match format: Indicates Test, ODI (One-Day International), or T20
Batting Statistics
For each batter, the scorecard shows:
- Name and runs scored: Individual contribution to team total
- Balls faced: How many deliveries they received
- Strike rate: Their scoring speed (runs per 100 balls)
- Boundaries: Number of fours and sixes hit
- Dismissal method: How they got out (caught, bowled, LBW, run out, etc.)
Bowling Analysis
For each bowler, you'll see:
- Overs bowled: Number of complete overs (sets of 6 balls)
- Maidens: Overs where no runs were scored
- Runs conceded: Total runs scored off their bowling
- Wickets taken: Number of batters dismissed
- Economy rate: Average runs conceded per over
Match Progress Indicators
- Fall of wickets: Shows the score when each wicket fell (e.g., "45-1" means first wicket at 45 runs)
- Partnerships: Runs scored between each pair of batters
- Extras breakdown: Details of wides, no-balls, byes, and leg-byes
- Total score: Final team score with wickets lost and overs used
How Cricket Scoreboards Display Live Information
A cricket scoreboard provides real-time match updates at a glance. Modern scoreboards, whether physical at the ground or digital online, display essential information:
Core Display Elements
- Current score: Team total and wickets lost (e.g., "156-3" means 156 runs for 3 wickets)
- Overs completed: Shows match progression (e.g., "23.4" means 23 overs and 4 balls)
- Required run rate: In chase situations, runs needed per over to win
- Individual scores: Current batters and their personal runs
Additional Information
- Recent overs: Runs scored in the last few overs
- Partnership details: Runs added by current batting pair
- Bowler statistics: Current bowler's figures for the match
- Target and equation: Runs needed from balls remaining
Digital Scoreboards Advantage
Using an online scoreboard for your own matches provides:
- Real-time updates viewable from anywhere
- Automatic calculation of run rates and statistics
- Professional appearance for broadcasts or streams
- Historical record of match data
Quick Reference: Cricket Scoring Essentials
Here's everything you need to remember about cricket scoring:
Scoring Methods
- Running: 1 run per successful sprint between wickets
- Boundaries: 4 runs (ball bounces) or 6 runs (no bounce)
- Extras: Additional runs from fielding team errors
Key Terms
- Innings: One team's turn to bat
- Over: Set of 6 balls bowled
- Wicket: Getting a batter out
- Strike rate: Scoring speed (runs per 100 balls)
- Economy rate: Bowler's runs conceded per over
Match Formats and Their Scoring Differences
- Test Cricket: Unlimited overs, both teams bat twice, highest total wins
- One-Day Cricket: 50 overs per team, single innings each
- T20 Cricket: 20 overs per team, emphasis on quick scoring